Chondroitin, which is a mucopolysaccharide, is present in the body in a form covalently bound to proteins. As an example, the conformation of chondroitin contained in the joint cartilage is shown in Fig. 3.
Fig. 3 Conformation of chondroitins contained in the joint cartilage.
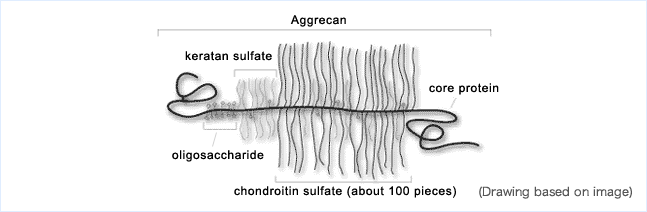
The cartilage consists of collagen, proteoglycan, cartilage cells, glucosamine, and water, and among them, the proteoglycan portion is constituted with hyaluronic acid, chondroitin, and proteins. The core proteins bound to the core of hyaluronic acid appear as a large number of hairs and assume a form like a brush. The hair-like part consists of oligosaccharide, keratan sulfate and chondroitin. Among them, as to which hairs are of chondroitin, the long hairs in the neighborhood of the end sections of the core protein are chondroitin. In this manner, about 100 chondroitins are bound to one core protein.
Furthermore, about 100 brushes of a core protein containing chondroitin are bound to the core of hyaluronic acid.
Copyright (C) ZERIA Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd. All Rights Reserved.






