Chondroitin sulfate (hereafter referred to as chondroitin) belongs to “glycan” (sugar chain) to which attention has begun to be paid in recent years as a life chain following proteins and nucleic acids (DNA) and is a substance representing mucopolysaccharides.
Glycan has a structure in which sugar units are chained. It is considered that the glycan is deeply involved in building block of our life activities such as the growth of cells, ageing of cells, immune functions, cancers, and virus infection by being bound to proteins and lipids, and we have expected that the glycan is expected to be applied to drug discovery and clinical applications in the future (Table 1).
Table 1
What the Glycan can be expected for drug discovery and clinical applications
| Functions of glycan | What can be expected |
|---|---|
| Identification of cells | Application to treatment for cancer and transplantation |
| Quality control | Development of drugs with long lasting efficacy |
| Protection of cells | Development of preservation liquid that does not damage the organs |
| Appropriate transport | Development of drugs for cerebral infarction and myocardiac infarction |
| Prevention of infection with pathogenic microorganisms | Development of drugs against influenza, SARS and other viral diseases |
![]()
Mucopolysaccharide is a polysaccharide containing amino sugar (a substance in which hydroxyl of a sugar molecule are replaced with amino groups) in the molecule, and since the mucopolysaccharide is present in a state in which it is bound to proteins, the mucopolysaccharide has recently been called proteoglycan, which means polysaccharide (glycan) having proteins (proteo) (Fig. 1). As a well-known mucopolysaccharide other than chondroitin, mention may be made of hyaluronic acid, which has been known well as a moisture-retaining component for cosmetics.
Fig. 1 Classification of Muco-polysaccharides
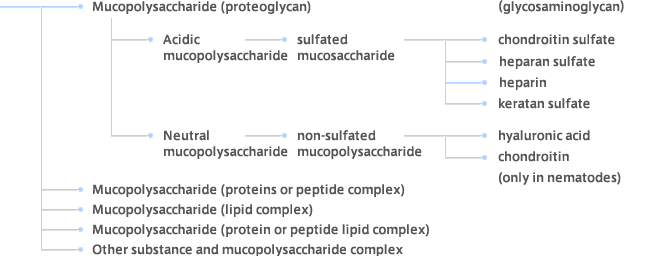
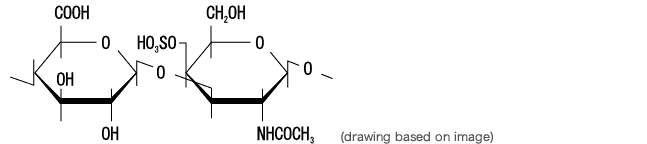
Fig. 2 Structure of chondroitin sulfate
Copyright (C) ZERIA Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd. All Rights Reserved.






